Private health insurance can help you pay hospital and medical costs not covered by Medicare. In some cases, you can receive treatment sooner by electing to be treated as a private patient. In Australia, private health insurance is ‘community rated’. This means that everyone is entitled to buy the same product, at the same price (except for Lifetime Health Cover and Age-based Discounts), and is guaranteed the right to renew their policy. A health insurer cannot refuse to insure you or refuse to sell you any policy you want to buy.
The choice of health cover is important, and is often considered as part of a suite of products that protect you and your family in the event of illness, loss of income, total or permanent disability, and death cover. Consideration of health cover and other products is important if you have a family and considerable financial obligations.
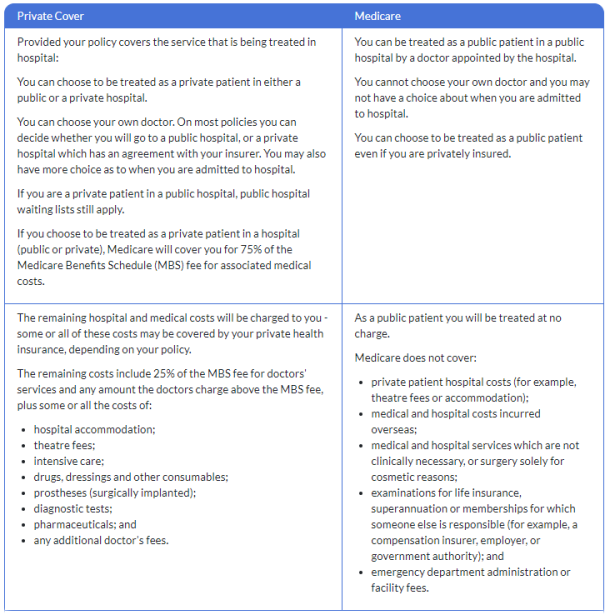
Private Health Cover versus Medicare
Hospital Cover
Medical Services and General Treatment
Pharmaceutical Cover
Ambulance Cover
The coverage tables are sourced from the Government’s PrivateHealth.gov.au  website.
website.
Types of Private Health Cover
There are three primary types of primary health cover:
- Hospital Policies Cover. Hospital policies cover you when you go to hospital.
- General Treatment Cover. General treatment policies (sometimes known as ancillary or extras) cover you for ancillary treatment (e.g. dental, physiotherapy).
- Ambulance Policies Cover. Ambulance policies cover you for ambulance transport.
Most health insurers offer combined policies that provide a packaged cover for both hospital and general treatment services, or you can buy separate hospital and general treatment policies to best fit your circumstances.
Health Cover Considerations
When considering appropriate private health cover, you should generally consider the following:
- Waiting periods. You will need to serve out a waiting period if taking cover for the first time. During this waiting period you will not be covered by any of the policy benefits. This is generally done to avoid frivolous claims.
- What isn’t covered on my policy. You should first determine what sort of cover is required, and then ensure your policy covers your primary requirements. However, it’s important to be aware of what features are not provided to you as part of a policy. It’s quite likely that out-of-pocket expenses would be expected for some types of cover.
- Healthcare Needs. You should review your cover from time to time to ensure it still meets your needs. Your requirements will change with age and other financial obligations (such as family).
The following video provides a general overview.
Government Surcharges & Incentives
The Australian Government provides the Private Health Insurance Rebate, and most consumers are eligible. There is an age-based discount that applies for those between the age of 18 and 29 and can result in significant lifetime costs on insurance. If you purchase hospital cover after the 1 July following your 31st birthday, you will have to pay the Lifetime Health Cover (LHC) loading on top of your premium. The loading increases for every year you are aged over 30.
More Information
THe Government provides a raft of resources on various types of private health cover  and limitations of universal Medicare. You should also make contact with us so we’re able to have a discussion based on your own circumstances.
and limitations of universal Medicare. You should also make contact with us so we’re able to have a discussion based on your own circumstances.